Enable Teachers
Enabling parents and professionals to become better teachers.


3rd Grade Math IEP Goal Bank Based On The Common Core Standards
Goal banks! Wahoo! This goal bank provides IEP goal examples based on the common core standards. If you are looking for more general “plug and chug” IEP goal formula’s check my other post out . These goals are only examples based on specific mathematical concept. You may need to modify how often they are measured, when they are tested, or simplify the related goal. Also keep in mind that sometimes students will be in a different grade level, but be working on a 3rd grade level skill. Your job as the teacher is to pick the goal type that fits with the student’s data driven needs.
I changed the way I measured goals frequently throughout. It is worth it to skim through each section and receive more ideas for wording and measuring goals!
Operations and Algebraic Thinking
Represent and solve problems involving multiplication and division.
Interpret products of whole numbers, e.g., interpret 5 × 7 as the total number of objects in 5 groups of 7 objects each. For example, describe a context in which a total number of objects can be expressed as 5 × 7 . CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.3.OA.A.1
Goal Example #1: Student will be able to independently describe one math scenario for a given multiplication problem on 10 individual trials, with 100% accuracy, through out the IEP year.
Goal Example #2 : Using a picture, student will be able to identify three math scenarios that would require a specific multiplication problem. Mastery of this skill will be completing an average accuracy rate of 90%, on a given test with 6 choices, across 3 consecutive trials
Interpret whole-number quotients of whole numbers, e.g., interpret 56 ÷ 8 as the number of objects in each share when 56 objects are partitioned equally into 8 shares, or as a number of shares when 56 objects are partitioned into equal shares of 8 objects each. For example, describe a context in which a number of shares or a number of groups can be expressed as 56 ÷ 8 . CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.3.OA.A.2
Goal Example #1: Student will be able to create a visual representation of a specific division problem (up to multiples of 5), with 80% accuracy across 8 out of 10 trials across one quarter.
Goal Example #2: Student will be able to read and identify a correct written scenario for a specific division problem. On a test with 3 trials, student will score an average of 80% accuracy, across 40 weekly trials.
Use multiplication and division within 100 to solve word problems in situations involving equal groups, arrays, and measurement quantities, e.g., by using drawings and equations with a symbol for the unknown number to represent the problem. CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.3.OA.A.3
Goal Example: Using a graphic organizer, student will be able to break down the three steps to solve a division word problem, with 80% accuracy across 10 weekly trials.
Determine the unknown whole number in a multiplication or division equation relating three whole numbers. For example, determine the unknown number that makes the equation true in each of the equations 8 × ? = 48, 5 = _ ÷ 3, 6 × 6 = ? CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.3.OA.A.4
Goal Example: Using a multiplication chart, student will be able to read a word problem about multiplication and write the mathematical sentence needed to solve the problem. Mastery will occur when student completes 3 out of 5 test questions, with an average of 80% accuracy across 40 trials.
Understand properties of multiplication and the relationship between multiplication and division.
Apply properties of operations as strategies to multiply and divide. 2 Examples: If 6 × 4 = 24 is known, then 4 × 6 = 24 is also known. (Commutative property of multiplication.) 3 × 5 × 2 can be found by 3 × 5 = 15, then 15 × 2 = 30, or by 5 × 2 = 10, then 3 × 10 = 30. (Associative property of multiplication.) Knowing that 8 × 5 = 40 and 8 × 2 = 16, one can find 8 × 7 as 8 × (5 + 2) = (8 × 5) + (8 × 2) = 40 + 16 = 56. (Distributive property.) CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.3.OA.B.5
Goal Example #1: Student will be able to match three examples of the commutative property with 4 out of 5 trials on with 80% accuracy, across 3 quarters.
Goal Example #2: When given a key, student will be able to identify commutative, associative, and distributive properties with 75% accuracy on 3 consecutive trials.
Understand division as an unknown-factor problem. For example, find 32 ÷ 8 by finding the number that makes 32 when multiplied by 8 . CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.3.OA.B.6
Goal Example #1: Given a multiplication table/graph, Student will be able to solve a division problem using multiplication skills with 80% accuracy across 3 out of 3 trials.
Goal Example #2: Student will be able to add multiples to find the answer to two digit by one digit division problems. This is mastered when student can do this independently with 90% accuracy on 3 consecutive trials.
Multiply and divide within 100
Fluently multiply and divide within 100, using strategies such as the relationship between multiplication and division (e.g., knowing that 8 × 5 = 40, one knows 40 ÷ 5 = 8) or properties of operations. By the end of Grade 3, know from memory all products of two one-digit numbers. CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.3.OA.C.7
Goal Example #1: Using a multiplication chart, student will be able to solve division problems up to 12 with 95% accuracy on 5 consecutive trials.
Goal Example #2: Student will be able to multiply double digit by double digit numbers with an average 70% accuracy on 3 trials each quarter this IEP year.
Solve problems involving the four operations, and identify and explain patterns in arithmetic
Solve two-step word problems using the four operations. Represent these problems using equations with a letter standing for the unknown quantity. Assess the reasonableness of answers using mental computation and estimation strategies including rounding. 3 CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.3.OA.D.8
Goal Example #1: Using a graphic organizer, solve two step addition word problems within numbers 1-100. Student will show mastery by solving these with 70% accuracy across 10 trials this IEP year.
Goal Example #2: Student will be able to identify which operation is being used (multiplication, division, addition, subtraction) with 80% accuracy averaged between their 10 most recent trials.
Identify arithmetic patterns (including patterns in the addition table or multiplication table), and explain them using properties of operations. For example, observe that 4 times a number is always even, and explain why 4 times a number can be decomposed into two equal addends . CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.3.OA.D.9
Goal Example #1: When given a set of numbers from the teacher, student will be able to identify if there is a pattern or not. Student will do this with 90% accuracy on 3 out of 5 trials.
Goal Example #2: Student will be able to create a picture to explain patterns with multiplication up to 100 with an average of 70% accuracy across 10 trials.
Check out these other third grade goal banks:
3rd Grade Reading
3rd Grade Writing
Thanks for your support! Let me know if there’s a way I can make these more accessible for you. I also take requests if you would like a certain set of goals published quicker. Keep up all the great work!
Share this:
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Tumblr (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window)
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window)
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
Discover more from Enable Teachers
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading

Math IEP Goals For Special Education

Drafting IEP goals can be difficult, so here are a few math IEP goals (across various ability levels) to get you started. Please adapt and modify to meet the specific needs of your students. Keep in mind a goal should be a skill you believe is achievable by the student in 1 school year. You can always do an addendum if a student has met all criteria for the goal/objectives.
Remember, when writing objectives, break down the goal into smaller steps. You can lessen the percentage of accuracy, the number of trials (3/5 vs 4/5), or amount of prompting. Just make sure the objectives build on each other and are working towards mastery.
The reason why I always list accuracy at 100% when writing Math goals is because the answer is either right or wrong, an answer to a math problem can’t be 50% correct. So feel free to play with the ## of trials for accuracy.
Number Identification:
Goal: Student will independently identify numbers 1-20 (verbally, written, or pointing) with 100% accuracy on 4 out of 5 trials measured quarterly.
Goal: When verbally prompted by teacher to “point to the number _________”, Student will independently select the correct number with 100% accuracy on 4 out of 5 trials measured quarterly.
Goal: Student will independently count in rote order numbers 1-25 with 100% accuracy on 4 out of 5 trials measured quarterly.
Goal: Student will independently count by 2, 3, 5, 10 starting from 0-30 verbally or written, with 100% accuracy on 4 out of 5 trials measured quarterly.
One-to-one Correspondence:
Goal: When given up to 10 objects, Student will independently count and determine how many objects there are (verbally, written, or by pointing to a number) with 100% accuracy on 4 out of 5 trials measured quarterly/monthly.
Goal: When given up to 10 items/objects, Student will independently count and move the items to demonstrate 1:1 correspondence and identify how many there are with 100% accuracy on 4 out of 5 trials measured quarterly.
Goal: Given 10 addition problems, Student will independently add single digit numbers with regrouping with 100% accuracy on 4 out of 5 trials as measured quarterly.
Goal: Student will independently add a single digit number to a double digit number with and without regrouping with 100% accuracy on 4 out of 5 trials measured quarterly.
Goal: Student will independently add double digit numbers to double digit numbers with (or without) regrouping with 100% accuracy on 4 out of 5 trials measured quarterly.
Adding with Number Line:
Goal: Given 10 addition problems and using a number line, Student will independently add single digit numbers with 100% accuracy on 4 out of 5 trials measured quarterly.
Subtraction:
Goal: Student will independently subtract a single digit number form a double digit number with and without regrouping with 100% accuracy on 4 out of 5 trials measured quarterly.
Goal: Given 10 subtraction problems, Student will independently subtract double digit numbers from double digit numbers with and without regrouping with 100% accuracy on 4 out of 5 trials measured quarterly.
Goal: Student will independently subtract money/price amounts from one another with and without regrouping, while carrying the decimal point with 100% accuracy on 4 out of 5 trials as measured quarterly.
Goal: Using a number line, Student will independently subtract numbers (20 or less) with 100% accuracy on 4 out of 5 trials measured quarterly.
Telling Time:
Goal: Student will independently tell time to the half hour on an analog clock (verbally or written) with 100% accuracy on 4 out of 5 trials measured quarterly.
Goal: Student will independently tell time to the hour on an analog clock (verbally or written) with 100% accuracy on 4 out of 5 trials measured quarterly.
Elapsed Time:
Goal: Given a problem with a start time and end time, Student will independently determine how much time has elapsed with 100% accuracy on 4 out of 5 trials measured quarterly.
Goal: Given a problem with a start time and duration of activity/event, Student will independently determine what the end time is with 100% accuracy on 4 out of 5 trials measured quarterly.
Dollar More:
Goal: Using the dollar more strategy, Student will independently identify the next dollar up when given a price amount with 100% accuracy on 4 out of 5 trials measured quarterly.
Goal: Student will independently identify the next dollar amount when given a price, determine how much is needed to make the purchase, and count out the necessary amount (using fake school money) with 100% accuracy on 4 out of 5 trials measured quarterly.
Goal: When given a price, student will identify which number is the dollar amount with 100% accuracy on 4 out of 5 trials measured quarterly.
Money Identification/Counting Money:
Goal: When given a quarter, dime, nickel, and penny, Student will identify the coin and corresponding value with 100% accuracy on 4 out of 5 trials measured quarterly.
Goal: When given a random amount of coins (all of one type), Student will independently count the coins with 100% accuracy on 4 out of 5 trials measured quarterly.
Goal: When given a mix of coins (to include quarter, dime, nickel, penny), Student will independently count the coins with 100% accuracy on 4 out of 5 trials measured quarterly.
Goal: When given a mixture of coins and dollar bills, Student will independently count the money with 100% accuracy on 4 out of 5 trials measured quarterly.
Goal: When give 2, 3, and 4 digit numbers, Student will independently round to the nearest tens, hundreds, thousands independently with 100% accuracy on 4 out of 5 trials measured quarterly.
Greater than/Less than:
Goal: Given 2 numbers, pictures, or groups of items, Student will independently determine which number is greater than/less than/equal by selecting or drawing the appropriate symbol (<,>, =) with 100% accuracy on 4 out of 5 trials measured quarterly.
Goal: Student will independently count objects or pictures of objects and tally the corresponding amount (up to 15) with 100% accuracy on 4 out of 5 trials as measured quarterly.
Goal: Given a number, up to 20, Student will independently tally the corresponding number with 100% accuracy on 4 out of 5 trials measured quarterly.
Goal: Given data and a bar graph template, Student will independently construct a bar graph to display the data and answer 3 questions about the data with 100% accuracy on 4 out of 5 trials measured quarterly.
Goal: Given a line, pie, or bar graph, Student will independently answer questions about each set of data with 100% accuracy on 4 out of 5 trials measured quarterly.
Goal: Given data and a blank graph template, Student will independently construct the graph to display the appropriate data with 100% accuracy on 4 out of 5 trials measured quarterly.
Goal: Student will independently identify the numerator and denominator in a fraction with 100% accuracy on 4 out of 5 trials measured quarterly.
Goal: When given a picture of a shape divided into parts, Student will independently color the correct sections in to represent the fraction given with 100% accuracy on 4 out of 5 trials measured quarterly.
Goal: Student will independently add fractions with like denominators with 100% accuracy on 4 out of 5 trials measured quarterly.
Word Problems:
Goal: Student will independently solve one step addition and subtraction word problems with 100% accuracy on 4 out of 5 trials measured quarterly.
Goal: Student will independently solve two step word problems (mixed addition and subtraction) with 100% accuracy on 4 out of 5 trials measured quarterly.
Goal: Student will independently solve one and two step multiplication world problems with 100% accuracy on 4 out of 5 trials measured quarterly.
Goal: Student will independently read a one or two step word problem, identify which operation is to be used, and solve it with 100% accuracy on 4 out of 5 trials measured quarterly.
Goal: Given a word problem, Student will independently determine which operation is to be used (+,-,x, /) with 100% accuracy on 4 out of 5 trials measured quarterly.
Even/Odd Numbers:
Goal: When given a number, student will independently identify if the number is odd or even (written or verbally), with 100% accuracy on 4 out of 5 trials measured quarterly.
Measurement:
Goal: Given varying lines and objects, Student will independently estimate the length of the object/picture, measure it using a ruler, and identify how long the object/picture is with 100% accuracy on 4 out of 5 trials measured quarterly.
Multiplication:
Goal: Student will independently solve 10 multiplication facts (2, 3, and 5 facts) with 100% accuracy on 4 out of 5 trials measured quarterly.
Goal: Student will independently solve 20 multiplication facts (facts up to 9) with 100% accuracy on 4 out of 5 trials measured quarterly.
Goal: Given a division problem (where the divisor is _____), Student will independently solve it with 100% accuracy on 4 out of 5 trials measured quarterly.
Feel free to use and edit as necessary. It’s up to you how often you want to measure the goals, but remind parents that even if the goal says 5/5 times quarterly, it doesn’t mean you’re only working on it those 5 times. That is just the number of times you’ll take official data. Just make sure it’s a reasonable ## so you have time to take all the data you need. Especially if you have multiple goals/objectives to take data for!
Happy drafting!
Where should we send your
Free lesson plans, success check your email for your free lessons.
We hate SPAM and promise to keep your email address safe.
Want some lesson plans you can immediately use?
Enter your email address below to get 5 free lesson plans now .
- Grades 6-12
- School Leaders
Check Out Today's Holiday Giveaway! 🎁
Free IEP Goal Bank With 110+ Goals and Printable Tracking Sheets
All the goals you need, when you need them.

There are as many IEP goals as there are students. But the longer you teach special education, the more you’ll find yourself searching for just the right reading comprehension goal for a student with a learning disability or a behavior goal for a kid who has ADHD. That’s where an IEP goal bank, also known as a goal database, comes in.
Below you’ll find a list of over 100 IEP goals covering a variety of focus areas. Plus be sure to fill out the form on this page to get access to a free, editable Google Doc version of the goal bank along with a bundle of free editable goal-tracking sheets. The bundle includes daily and weekly goal-tracking sheets, as well as trial tracking and progress tracking sheets for data collection.
IEP Goals 101
- Reading Comprehension Goal Bank
- Math Goal Bank
- Writing Goal Bank
- Behavior Goal Bank
- Social Skills Goal Bank
- Social-Emotional Goal Bank
- Executive Functioning Goal Bank
- Self-Advocacy Goal Bank
IEP goals should be specific enough to be implemented by anyone who reads them. They should address aspects of the general curriculum but at the student’s functional level. And the goals should be actionable and measurable.
The goals should also include the accuracy and number of trials that the student needs to complete to show mastery. The accuracy and number of trials will depend on the student’s ability, strengths, and skills. (Typical accuracy and trials are 80% 4-out-of-5 trials.)
Finally, the goals should include the level of support the student needs. Should they be demonstrating the skill independently, or do they need a few prompts or maximum support? Build that into the goal too.
So, a finished goal might be: When given a pile of coins (all one type), Jaime will count the coins and find the total with no more than two prompts with 70% accuracy in 3 out of 5 trials.
IEP Goals for Your Database
A lot of thought goes into each IEP goal, so here are more than 100 goals that every special education teacher should have in their bank.
Reading Comprehension IEP Goal Bank
Reading comprehension is a skill that many students struggle with it. Choose a goal that helps students reach the next level of reading comprehension so they can understand and enjoy what they read.
- When given a story at their reading level, [STUDENT] will use a storyboard or story map to outline the story’s main elements.
- When given a nonfiction text at their reading level, [STUDENT] will select and use the appropriate graphic organizer to identify key information.
- When given a paragraph at their reading level, [STUDENT] will apply the RAP strategy ( R eading a single paragraph, A sking oneself to define the main idea and supporting details, P utting the information into the reader’s language).

- When given a passage at their reading level, [STUDENT] will use an outline strategy to summarize the content or retell the story.
- When given a text at their reading level, [STUDENT] will read and demonstrate literal knowledge by answering five literal questions.
- [STUDENT] will demonstrate understanding of text using total communication (AAC devices, PECS, verbalization, sign language) to answer five literal questions about the text.
- When presented with a passage at their reading level, [STUDENT] will use context clues to identify the meaning of unknown words.
- When given a passage at their instructional level, [STUDENT] will make a prediction and read to confirm or adjust their prediction with information from the text.
- When given a text at their reading level, [STUDENT] will identify the main idea and two supporting details.

- Given a sentence, [STUDENT] will combine background knowledge with information from the text to infer the author’s meaning.
- Given a passage at their reading level, [STUDENT] will answer five inferential questions.
- After reading a passage with visual supports (e.g., highlighting), [STUDENT] will answer literal questions with minimal assistance.
- After reading a passage at their reading level, [STUDENT] will identify the author’s purpose for writing.
- Given a list of author’s purposes and a text, [STUDENT] will select the correct author’s purpose for writing.
Math IEP Goal Bank
Students may be working on numeracy or word problems. Whatever their focus, choose a math goal that helps them progress. ADVERTISEMENT
- [STUDENT] will identify a one- or two-digit number (verbally, pointing, written).
- [STUDENT] will rote-count from 1 to 25 (or higher).
- [STUDENT] will skip-count by 2, 3, 5, 10 to 50 (verbal or written).
![math problem solving iep goals for 3rd grade When given up to 10 objects, [STUDENT] will count and state how many objects there are (verbally, pointing).](https://www.weareteachers.com/wp-content/uploads/3-44.jpg)
- Given 10 addition problems, [STUDENT] will independently add single-digit numbers with (or without) regrouping.
- [STUDENT] will independently subtract a single-digit number from a double-digit number with (or without) regrouping.
- Given 10 subtraction problems, [STUDENT] will independently subtract double-digit numbers from double-digit numbers with (or without) regrouping.
- [STUDENT] will independently tell time to the half hour (or quarter hour, etc.) on an analog clock (verbal or written).
- [STUDENT] will independently identify the next dollar amount when given a price, determine how much is needed to make a purchase, and count out the necessary amount using school money.
- Given a quarter, dime, nickel, and penny, [STUDENT] will identify the coin and value.
- Given a random amount of coins (all one type or mixed), [STUDENT] will independently count the coins.

- When given two-digit (or three- or four-digit) numbers, [STUDENT] will round to the nearest tens (or hundreds or thousands).
- Given two numbers (pictures, groups of items), [STUDENT] will determine which number is greater than/less than/equal to by selecting or drawing the appropriate symbol.
- Given data and a graph (bar, pie), [STUDENT] will complete the graph to display the data.
- Given a graph (bar, pie, line), [STUDENT] will answer three questions about the data.
- [STUDENT] will identify the numerator and denominator in a fraction.
- When given a picture of a shape divided into parts, [STUDENT] will color the correct number of sections to represent the fraction given.

- [STUDENT] will solve one-step word problems using addition and subtraction (or multiplication and division).
- [STUDENT] will independently solve 15 multiplication facts (up to 9).
- Given a fact-fluency tracker, [STUDENT] will track mastery of multiplication facts up to 12.
- Given a problem-solving checklist, [STUDENT] will use the checklist to solve a one-step or two-step word problem.
Writing IEP Goal Bank
Here are writing IEP goals for organization, fluency, and editing.
- Given a topic, [STUDENT] will write a sentence that accurately addresses the topic.
- Given a word bank, [STUDENT] will select the appropriate words to complete a sentence or paragraph about a topic.
- [STUDENT] will use a keyword outline to write a paragraph with at least [number of] sentences, including an introduction/topic sentence and conclusion sentence.

- [STUDENT] will dictate a response to a question and use talk-to-text to communicate at least three sentences about a topic.
- [STUDENT] will write a three-paragraph essay about a topic that includes a clear introductory sentence, main idea, supporting details, and conclusion.
- [STUDENT] will select and use the appropriate graphic organizers to organize ideas in response to a writing topic.

- When given a paragraph to revise, [STUDENT] will add transitional words and phrases to connect ideas in sentences (or paragraphs).
- When given a prompt, [STUDENT] will maintain writing for [amount of time] as measured by observation and student writing output.

Behavior IEP Goal Bank
Everything we see in school is behavior, from working to engaging in class to maintaining self-control and managing emotions. If a student has an IEP for ADHD, an emotional disability, autism, or other categories, they may be working on behavior goals to improve their ability to succeed in school.
- Given a self-monitoring checklist, [STUDENT] will demonstrate self-regulation during [# of sessions] across [# of months].

- Given a token board, [STUDENT] will follow class rules to earn [# of tokens] for each 30-minute period in special and general education settings.
- Given a self-regulation strategy (e.g., zones of regulation), [STUDENT] will identify when they are moving from green to red, and apply a self-regulation strategy to maintain their self-regulation.
- Given support and a visual model, [STUDENT] will implement an organizational system for their locker/desk/backpack/binder.

- Given scripts and reminders, [STUDENT] will manage frustration and disruptions to their routine during classroom activities.
- Given a social story, [STUDENT] will be able to adjust to new routines and procedures in the classroom.
- By the end of the IEP, [STUDENT] will manage conflicts, independent of teacher support, 4 out of 5 occurrences over a ___ time period.
- Given a work assignment, [STUDENT] will initiate work tasks as measured by observation and work completion.
- Given a work assignment, [STUDENT] will complete work tasks as measured by observation and work completion.
- Given a token board and visual or rules, [STUDENT] will follow rules and earn tokens throughout the total school environment.
Social Skills IEP Goal Bank
Social skills may not seem academic, but how students engage with others can be an important outcome for students who have deficits in this area. Here are goals that can support their progression in forming relationships with peers and adults.
- During unstructured class time, [STUDENT] will engage in respectful conversation with peers (maintain personal space, use respectful voice).
- During unstructured class time or play time (e.g., recess), [STUDENT] will engage with peers (participate, share, follow rules, take turns) for > 10 minutes with minimal adult prompting.

- During a preferred activity, [STUDENT] will invite a peer to join in during recess.
- During a preferred activity, [STUDENT] will engage in appropriate conversation (ask appropriate questions, respond to questions, take turns) for > five turns.
- When frustrated or involved in a conflict, [STUDENT] will resolve the conflict without aggression but will apply a problem-solving strategy (walk away, tell a teacher).
- [STUDENT] will demonstrate five back-and-forth exchanges with peers during structured play activities.

- [STUDENT] will engage in appropriate turn-taking with peers in classroom discussion.
- [STUDENT] will decrease inappropriate verbal comments to once per day (or week) or less as measured by teacher observation and behavior checklist.
- Given a pre-activity checklist, [STUDENT] will identify one peer they would like to engage with and how they are going to engage (e.g., ask a question, invite to play).
Social-Emotional Skills IEP Goal Bank
Identifying and managing feelings is another important school outcome for students who have deficits in this area. Here are goals that help students advance in social-emotional skills.
- [STUDENT] will work cooperatively with peers in small-group settings (e.g., share materials, engage in conversation, accept others’ ideas).

- [STUDENT] will identify appropriate social rules and expectations for various social situations.
- [STUDENT] will refrain from interrupting others.
- [STUDENT] will identify emotions presented in picture form.

- [STUDENT] will engage in communication with others by asking questions when provided with the opportunities.
- [STUDENT] will increase or maintain conversation about a preferred or nonpreferred topic.
- Given a strategy and visual prompts, [STUDENT] will identify the signs of anxiety and apply a strategy to address feelings of anxiety in real and simulated situations.
- Given a picture scale, [STUDENT] will identify the level of anxiety they are feeling.
Executive Functioning IEP Goal Bank
Executive functioning skills are skills like planning, working memory, attention, problem-solving, mental flexibility, and self-regulation that help kids be successful in school. Students with poor executive functioning have a hard time with time management, organization, getting started with or finishing work, and connecting past experiences with current actions. (Know any kids like this?) Here’s a list of goals for helping students with executive functioning.
- Given visual cues, [STUDENT] will implement a system for organizing their backpack (locker, binder).
- Given a task and a list of materials, [STUDENT] will gather the needed items to complete the task.

- [STUDENT] will arrive at class with necessary materials (paper, pen, computer).
- [STUDENT] will use a checklist (visual schedule) to independently complete classwork.
- [STUDENT] will respond appropriately to oral commands.
- [STUDENT] will ask for clarification and further explanation when needed.
- [STUDENT] will request desired objects or instructional materials and equipment using [picture prompts, sign language, AAC device, etc.].

- [STUDENT] will express needs, wants, and feelings using [picture prompts, sign language, verbalization, etc.].
- [STUDENT] will create a daily visual schedule (or checklist or to-do list) and complete it.
- By the end of the IEP, [STUDENT] will demonstrate the ability to follow multiple-step directions (two or three steps) with minimal (one or two) adult prompts.
- By the end of the IEP, [STUDENT] will refer to their checklist for task completion to finish assigned work.
Self-Advocacy IEP Goal Bank
Self-advocacy goals are for skills from decision-making to goal attainment, asking for help, and speaking up for yourself. These are important skills that students need to develop, especially as they transition into independent living, college, and career.
- [STUDENT] will effectively communicate their needs and preferences in the classroom by [raising their hand, writing a note].
- [STUDENT] will use a communication notebook to write questions and concerns to the teacher one time per week.
- [STUDENT] will identify a goal, create a list of steps to achieve the goal, and work through the steps.
- Given a challenging situation to solve, [STUDENT] will define the problem and come up with two possible solutions.
- Given a task that involves a choice (e.g., the school lunch menu, a list of books), [STUDENT] will select between the options available.
![IEP-Goal-Bank-16 Given a task that involves a choice (e.g., the school lunch menu, a list of books), [STUDENT] will select between the options available.](https://www.weareteachers.com/wp-content/uploads/IEP-Goal-Bank-16.jpg)
- [STUDENT] will create a list of three personal strengths and three areas for improvement.
- [STUDENT] will actively participate in the development of their IEP goals and accommodations.
- [STUDENT] will identify one IEP goal and three objectives to support that goal.
- When faced with an academic challenge, [STUDENT] will seek assistance by raising their hand or using the classroom procedure for seeking help.
- [STUDENT] will advocate for accommodations and/or modifications in the classroom using an appropriate time, tone of voice, and language.
- [STUDENT] will demonstrate understanding of their learning preferences using a checklist, verbal communication, or another method of communication.
- [STUDENT] will engage in positive self-talk daily with and without teacher support.
- By the end of the IEP, [STUDENT] will learn and apply two self-advocacy strategies.
![IEP-Goal-Bank-17 By the end of the IEP, [STUDENT] will learn and apply two self-advocacy strategies.](https://www.weareteachers.com/wp-content/uploads/IEP-Goal-Bank-17.jpg)
- By the end of the IEP, [STUDENT] will demonstrate the ability to ask for help when needed.
- By the end of the IEP, [STUDENT] will identify and communicate two environmental requirements (e.g., “I need a movement break”).
- By the end of the IEP, [STUDENT] will engage in three conferences and/or meetings where the student will communicate their educational needs.
- [STUDENT] will explain and advocate for testing accommodations through the classroom teacher, testing center, school counselor, etc.
- [STUDENT] will reflect on their academic progress and will determine which accommodations are supporting their learning.
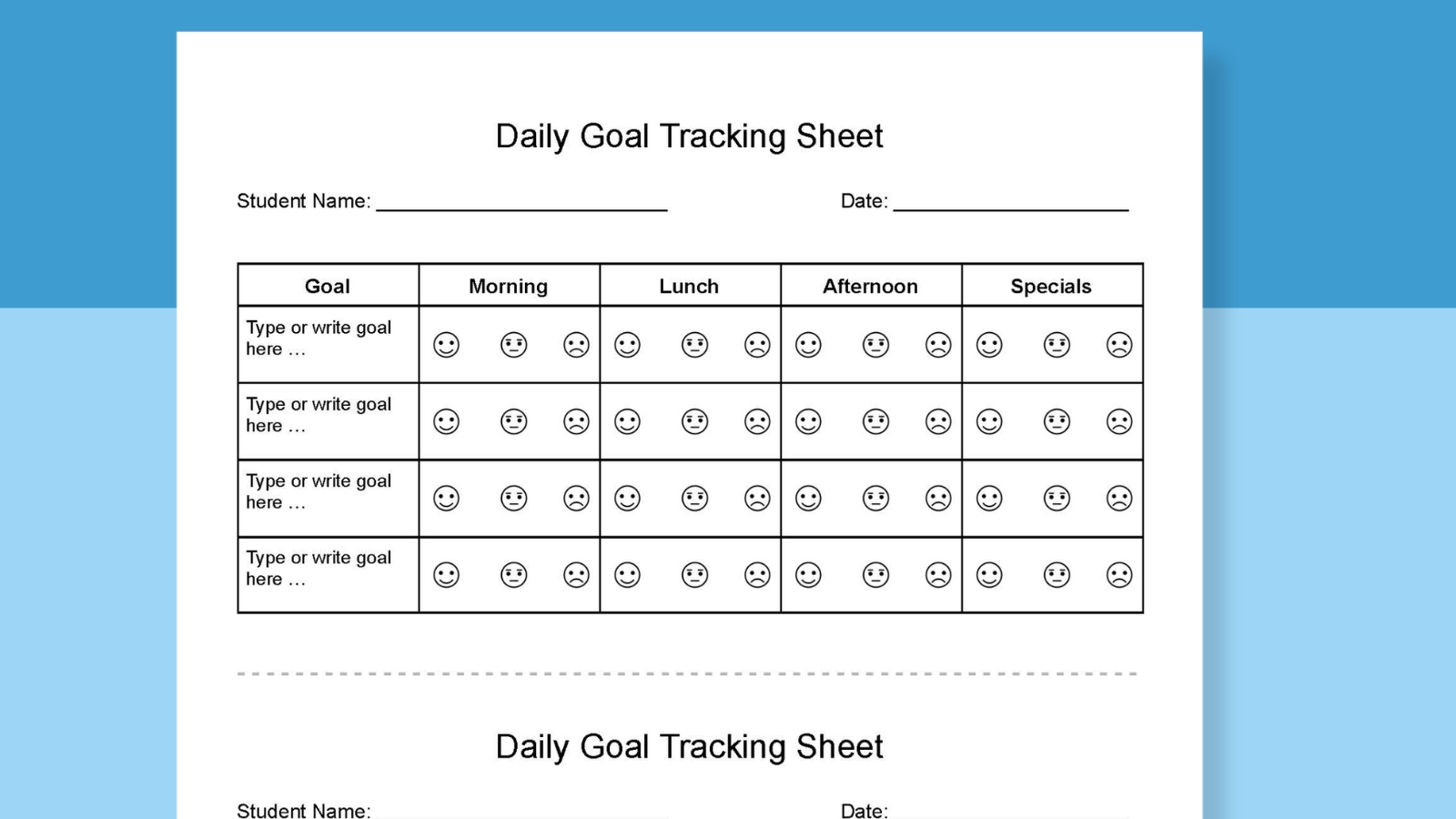
Get Your Free Editable and Printable IEP Goal Bank and Goal Sheets
Just fill out the form on this page to get instant access to an editable Google Doc with all the goals mentioned above as well as a bundle of four printable and editable goal-tracking sheets. Save your goal bank and access it any time to cut and paste goals into your IEP software and/or into the editable and printable goal-tracking sheets provided. The bundle includes daily and weekly tracking sheets, as well as trial tracking and progress tracking sheets for data collection.
Special education teachers are the best! Here are our favorite TikToks to make you feel seen .
Share your special education stories and connect with other teachers in our we are teachers helpline group on facebook., you might also like.
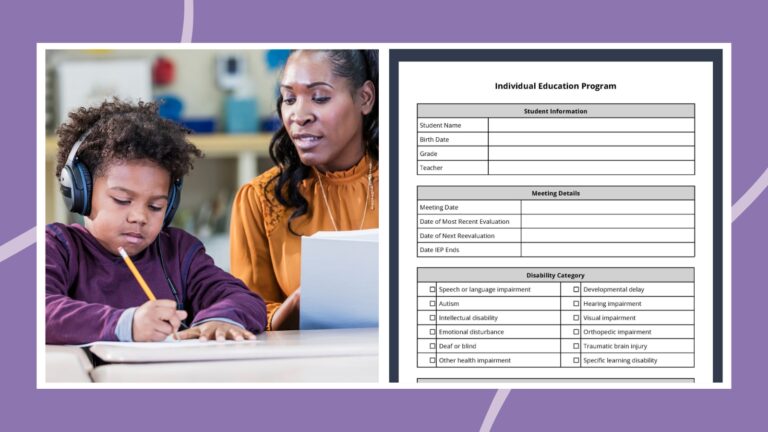
Free IEP Template (Fully Editable and Printable)
Everything you need to write a personalized IEP. Continue Reading
Copyright © 2024. All rights reserved. 5335 Gate Parkway, Jacksonville, FL 32256

5 Major 3rd Grade Math IEP Goals Special Education | TeachTastic IEPs
Updated: Apr 21
Are you a 3rd-grade math teacher who hates writing iep goals?
TeachTastic has the perfect math goals for 3rd grade . You won’t have to waste time writing them on your own anymore! These quarterly objectives are written with full-year learning progression in mind. This saves time when everything is already mapped out and all you have to do is teach.

Five Major Goals for 3rd-Grade Math
All students, regardless of ability level, are held to the same Common Core Standards or individual state standards in third grade math. However, for students with special needs, there are five major goals that must be accomplished in order to ensure success in the coming 4th-grade curriculum. These goals include mastering multiplication skills, being able to solve word problems, and being proficient in addition and subtraction within 1000. By accomplishing these goals, special education students will be prepared for success in all future grade levels.
Here are those goals, as well as a look at how they reflect the needs of special education students in general. These are not specific to one standard or another but rather what all states generally agree on as five major goals or math skills to master.
Addition and subtraction within 1000
Multiplication facts products of whole numbers
Place value up to three digits
Write a fraction to a model, and model to fraction interchangeably
Tell and write time to the nearest minute
Addition and subtraction within 1000:
One of the most important things that students need to master in 3rd grade is addition and subtraction within 1000. This goal includes mastering addition and subtraction facts within this range, as well as being able to solve problems using these operations. By mastering these skills, students will be able to solve more complex math problems with ease.
By (date), when given two three-digit numbers with sums no greater than 1000, the student will add numbers to find the sum , improving addition skills from 0/10 work samples out of ten consecutive trials to 8/10 work samples in ten consecutive trials.
Multiplication and division facts:
In order to understand more complex mathematical concepts, students learn a strong foundation in multiplication and division facts. These skills are essential for solving problems and mastering more difficult concepts in later grades. Teaching these facts in 3rd grade will help ensure that your students are prepared for the challenges ahead.
By (date), when given problems with multiplication, the student will interpret products of whole numbers, e.g., interpret 5 × 7 as the total number of objects in 5 groups of 7 objects each , improving operations and algebraic thinking skills from 0/10 work samples out of ten consecutive trials to 8/10 work samples in ten consecutive trials.

A big part of math at this grade level is introducing students to multiplication. IEP goals for third-grade multiplication include having students use array models to show equal groups. This helps them connect the dots between the equal groups and the visual representation of what it is to multiply. It also allows them to see how arrays can help solve word problems with situations involving equal groups. In other words, equal groups are a key component in understanding multiplication.
Lesson plans on multiplication with arrays can be a great way to help students learn and practice their math skills. An array is a set of numbers that are arranged in rows and columns. To multiply using an array, you need to find the product of the numbers in each row and column. For example, if you have an array with 2 rows and 3 columns, you would multiply 2x3 to get 6. You can then use this same method to teach lesson plans on multiplication with arrays with more rows and columns. This can be a great way to help students learn and practice their math skills. equal groups means that there are an equal number of items in each group. This is often used when dividing items into groups as well.
Once students have a firm grasp of array models, they can begin to apply their multiplication skills to solve problems involving the multiplication of larger numbers including decimals and fractions. By the end of third grade, students should be able to confidently multiply with array models to show equal groups.
Free multiplication chart/multiplication table for 3rd math | TeachTastic Publishing
Place value up to three digits:
Understanding place value is essential for mastering more complex mathematics concepts. In 3rd grade, students should be able to understand and work with numbers up to three digits. This understanding will lay the foundation for success in later grades and beyond.
Many special education lesson plans focus on teaching the round whole numbers to the nearest 10 or 100. This skill is essential for mastering all future mathematics concepts including many life skills. In addition, it helps students to develop number sense and understand place value. Round whole numbers can be taught using a variety of methods, including number lines, counters, and manipulative objects. However, it is important to choose a method that is appropriate for the student's level of understanding.
By (date), when given problems with place value, the student will round whole numbers to the nearest 10 or 100 , improving numbers and operation in based ten skills from 0/10 work samples out of ten consecutive trials to 8/10 work samples in ten consecutive trials.
Fractions and decimals to tenths:
By 3rd grade, students should be able to understand fractions and decimals in terms of tenths. This understanding will help them solve problems and work with more complex fractions and decimals later on.
By (date), when given a fraction or model, the student will write a fraction to a model, and model to fraction interchangeably , improving fraction skills from 0/10 work samples out of ten consecutive trials to 8/10 work samples in ten consecutive trials.
Measurement:
In 3rd grade, students should start to develop an understanding of measurement. This includes concepts such as length, weight, capacity, and time. Developing a strong foundation in measurement will help students throughout their school career and beyond.
By (date), when given a clock, the student will tell and write time to the nearest minute , improving measurement of time skills from 0/10 work samples out of ten consecutive trials to 8/10 work samples in ten consecutive trials.

Teaching telling and writing time to the nearest minute is an essential life skill for all students, including those with special needs. Being able to tell time is a necessary life skill that helps people function independently. It is also an important mathematical skill, as it helps develop an understanding of concepts like measurement and estimation. For students with special needs, telling time can be especially challenging. However, there are some effective strategies that special education teachers can use to help their students master this skill. One approach is to use visual aids, such as clocks and calendars, to help students understand the concept of time.
All of these goals are essential for students to learn in 3rd grade. However, they are not the only skills that students need to learn. There are many other important concepts and skills that students should learn in order to be successful in math. These include but are not limited to:
Knowing how to read and write a number line
Understanding what operations can be performed with addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division
Being able to solve word problems
Understanding concepts of geometry and measurement
We know that teachers don’t have time to waste, which is why we created these free must-have IEP math goals for 3rd grade. They save you time when all you need is something that works perfectly from day one of teaching this quarter. It will make your life easier and more productive, so what are you waiting for?
TeachTastic has created a 3rd Grade Math IEP Goals for K-3 that are unique and can be tailored to your needs. The five major goals listed above cover the basics of what any student with an Individualized Education Program (IEP) must accomplish by the end of third grade, whether they're in special education or not. These yearly objectives will save you time when everything is already mapped out and all you have to do is teach!
This article was written by TeachTasticiep, a mathematics education expert and curriculum developer.
For more information, please visit our goal bank
Find us on social media for all the latest updates to goals and special education align digital products. Facebook
Related Posts
25 IEP Goals for Supporting ADHD Through Organization Skills | TeachTastic
Related Products

Lesson Plan & Worksheet Pack - Change Between Standard and Expanded Form - 4908

Write the Room: Change Between Standard and Expanded Form - 4908

TeachTastic Center: Change Between Standard and Expanded Form - 4908

Lesson Plan & Worksheet Pack: Place Value Names Up to Ten Thousands - 7409

TeachTastic Center: Determine Place Value Names Up to Ten Thousands - 7409

Write the Room: Determine Place Value Names Up to Ten Thousands - 7409

IEP Goal Workbook - Multiply and Divide to 100 - 7553

Division Input and Output Tables Lesson Plan & Worksheet Pack - 7553

Write the Room: Complete Division Input and Output Tables - 7553

TeachTastic Center: Division Input and Output Tables - 7553

Lesson Plan & Worksheet Pack - Division Number Sentences Are True/False - 7552

Write the Room: Determine If Division Number Sentences Are True or False - 7552

Center: Determine If Division Number Sentences Are True or False - 7552

Division Facts Lesson Plan & Worksheet Pack - 7551

Lesson Plan & Worksheet Pack: Determine if Facts Are True or False - 7550

Write the Room: Determine if Division Facts Are True or False - 7550

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
By the end of Grade 3, know from memory all products of two one-digit numbers. CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.3.OA.C.7. Goal Example #1: Using a multiplication chart, student will be able to solve division problems up to 12 with 95% accuracy on 5 consecutive trials.
Objective: By the end of the IEP period, the student will be able to solve multi-step math word problems involving addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division with numbers up to 100, demonstrating understanding of the problem-solving process and achieving at least 70% accuracy on problem-solving tasks administered monthly.
Math IEP goals for third grade: Scaffolded IEP goal objectives target word problems, place value, rounding, multiplication, and division, ensuring student success. ... Solve Problems Using Multiplication Properties. Understand Properties of Multiplication. Use the Distributive Property to Find Missing Factors.
List of Math Problem Solving IEP goals for all ages and grades. List of Math Problem Solving IEP goals for all ages and grades. Skip to content. Become a Special Education Advocate ... Spectrum Math Word Problems Grade 2, Ages 7 to 8, 2nd Grade Math… Sold as 1 Each. Carson-Dellosa Publishing 2013. 10.80 x 8.40 x 0.26. $7. Save Add to Cart ...
Goal: Given a division problem (where the divisor is _____), Student will independently solve it with 100% accuracy on 4 out of 5 trials measured quarterly. Feel free to use and edit as necessary. It's up to you how often you want to measure the goals, but remind parents that even if the goal says 5/5 times quarterly, it doesn't mean you ...
Goal: By the end of the IEP period, student will solve math word problems with 90% accuracy and within a reasonable time frame. Word Problem Teaching Strategies and Accommodations Remember that a student will need a certain level of executive functioning skills to do math word problems.
Math IEP goals for third grade: Scaffolded IEP goal objectives target word problems, place value, rounding, multiplication, and division, ensuring student success. Take action now to support academic growth! top of page. ... Use Properties to Solve Addition Problems. Grade.
Measurable Mathematics Standards Based IEP Goals for 3rd grade Third Grade Goals Strand/Standard Strategies/Ideas for Instruction Given 10 problems involving the sum or difference of two whole numbers, each 9,999 or less, with or without regrouping, the student will solve with 80% accuracy using various computational methods by annual review of ...
All Grades K-5 All Grades 6-12 PreK 6th Grade Kindergarten 7th Grade 1st Grade 8th Grade 2nd Grade 9th Grade 3rd Grade 10th Grade 4th Grade 11th Grade 5th Grade 12th Grade. ... Math IEP Goal Bank. Students may be working on numeracy or word problems. Whatever their focus, choose a math goal that helps them progress. ... Given a problem-solving ...
These goals include mastering multiplication skills, being able to solve word problems, and being proficient in addition and subtraction within 1000. By accomplishing these goals, special education students will be prepared for success in all future grade levels. ... TeachTastic has created a 3rd Grade Math IEP Goals for K-3 that are unique and ...