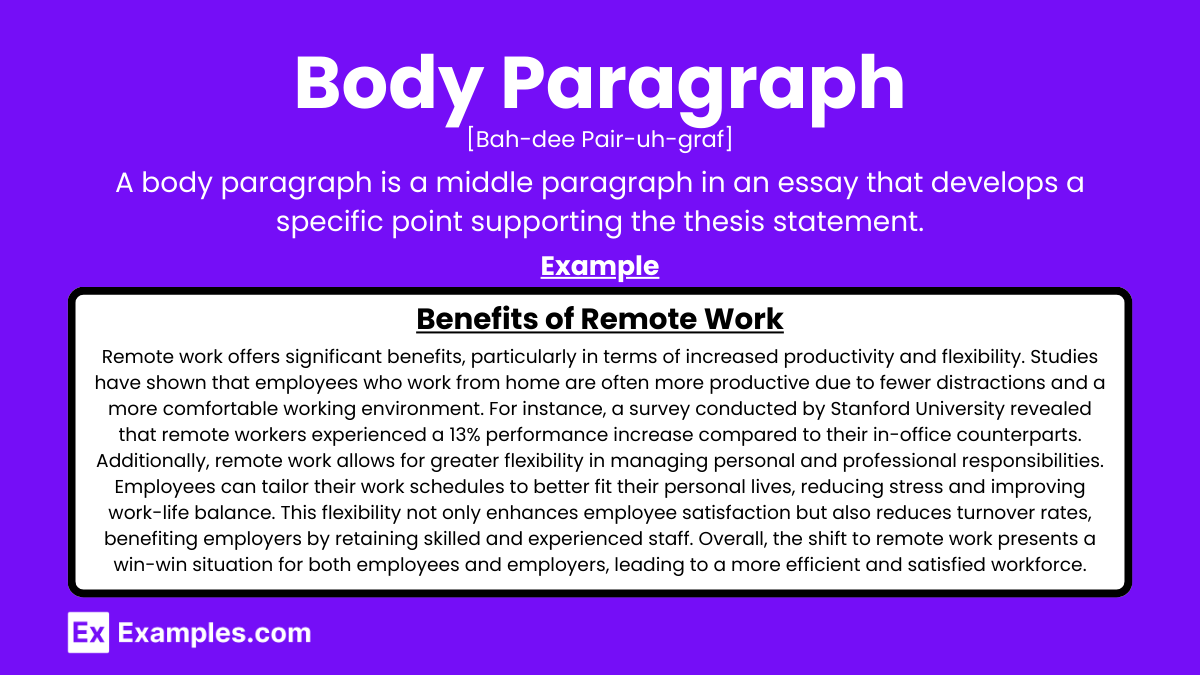
Body Paragraph
Definition of body paragraph.
A body paragraph in an essay is a paragraph that comes between the introduction and the conclusion . In a five-paragraph essay, there are three body paragraphs, while in longer essays there could be five or even ten. In major research papers, there are hundreds of body paragraphs.

Components of a Body Paragraph
A body paragraph has three major components: (1) topic sentence , (2) explanation, (3) supporting details. Without any of them, the body paragraph seems to be missing something, and will not add anything to the theme and central idea of the essay.
- Topic Sentence The topic sentence is the first sentence of a paragraph, and states the main idea to be discussed in the paragraph. In a body paragraph, the topic sentence is always about the evidence given in the thesis statement of the essay. It could be a claim , an assertion , or a fact needing explanation. It is generally a statement or a declarative sentence.
- Explanation / Example The topic sentence is followed by an explanation and/or an example. Whatever it is, it generally starts with “in other words” or “it means;” or “for example,” “for instance,” etc. This is called “metacommentary,” or telling of the same thing in different words to explain it further, so that readers can understand.
- Supporting Details Supporting details include concrete examples, rather than explanation or metacommentary. In common essays, or five-paragraph essays, this is just a one-sentence example from everyday life. However, in the case of research essays, these are usually quotes and statistics from research studies.
Different Between an Introduction and a Body Paragraph
Although both are called paragraphs, both are very different from each other not only in terms of functions but also in terms of components. An introduction occurs in the beginning and has three major components; a hook , background information , and a thesis statement . However, a body paragraph is comprised of a topic sentence making a claim, an explanation or example of the claim, and supporting details.
Examples of Body Paragraph in Literature
Example #1: autobiography of bertrand russell (by bertrand russell).
“Three passions, simple but overwhelmingly strong, have governed my life: the longing for love, the search for knowledge, and unbearable pity for the suffering of mankind. These passions, like great winds, have blown me hither and thither, in a wayward course, over a great ocean of anguish, reaching to the very verge of despair. I have sought love, first, because it brings ecstasy – ecstasy so great that I would often have sacrificed all the rest of life for a few hours of this joy. I have sought it, next, because it relieves loneliness – that terrible loneliness in which one shivering consciousness looks over the rim of the world into the cold unfathomable lifeless abyss. I have sought it finally, because in the union of love I have seen, in a mystic miniature, the prefiguring vision of the heaven that saints and poets have imagined. This is what I sought, and though it might seem too good for human life, this is what – at last – I have found.”
This is a paragraph from the prologue of the autobiography of Bertrand Russell. Check its first topic sentence, which explains something that is further elaborated in the following sentences.
Example #2: Politics and the English Language (by George Orwell)
“The inflated style itself is a kind of euphemism . A mass of Latin words falls upon the facts like soft snow , blurring the outline and covering up all the details. The great enemy of clear language is insincerity. When there is a gap between one’s real and one’s declared aims, one turns as it were instinctively to long words and exhausted idioms , like a cuttlefish spurting out ink. In our age there is no such thing as ‘keeping out of politics.’ All issues are political issues, and politics itself is a mass of lies, evasions, folly, hatred, and schizophrenia. When the general atmosphere is bad, language must suffer. I should expect to find — this is a guess which I have not sufficient knowledge to verify — that the German, Russian and Italian languages have all deteriorated in the last ten or fifteen years, as a result of dictatorship.”
This paragraph has a very short topic sentence. However, its explanation and further supporting details are very long.
Function of Body Paragraph
The elements of a body paragraph help to elaborate a concept, organize ideas into a single whole, and help bridge a gap in thoughts. The major task of a body paragraph is the organization of thoughts in a unified way. It also helps an author to give examples to support his claim, given in the topic sentence of that body paragraph. A good paragraph helps readers understand the main idea with examples.
Related posts:
- I Sing the Body Electric
- Simple Paragraph
Post navigation

TOPIC SENTENCE/ In his numerous writings, Marx critiques capitalism by identifying its flaws. ANALYSIS OF EVIDENCE/ By critiquing the political economy and capitalism, Marx implores his reader to think critically about their position in society and restores awareness in the proletariat class. EVIDENCE/ To Marx, capitalism is a system characterized by the “exploitation of the many by the few,” in which workers accept the exploitation of their labor and receive only harm of “alienation,” rather than true benefits ( MER 487). He writes that “labour produces for the rich wonderful things – but for the worker it produces privation. It produces palaces—but for the worker, hovels. It produces beauty—but for the worker, deformity” (MER 73). Marx argues capitalism is a system in which the laborer is repeatedly harmed and estranged from himself, his labor, and other people, while the owner of his labor – the capitalist – receives the benefits ( MER 74). And while industry progresses, the worker “sinks deeper and deeper below the conditions of existence of his own class” ( MER 483). ANALYSIS OF EVIDENCE/ But while Marx critiques the political economy, he does not explicitly say “capitalism is wrong.” Rather, his close examination of the system makes its flaws obvious. Only once the working class realizes the flaws of the system, Marx believes, will they - must they - rise up against their bourgeois masters and achieve the necessary and inevitable communist revolution.
Not every paragraph will be structured exactly like this one, of course. But as you draft your own paragraphs, look for all three of these elements: topic sentence, evidence, and analysis.
- picture_as_pdf Anatomy Of a Body Paragraph
Purdue Online Writing Lab College of Liberal Arts
Body Paragraphs

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
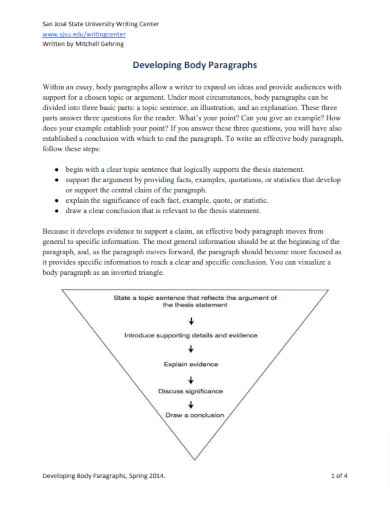
Body paragraphs: Moving from general to specific information
Your paper should be organized in a manner that moves from general to specific information. Every time you begin a new subject, think of an inverted pyramid - The broadest range of information sits at the top, and as the paragraph or paper progresses, the author becomes more and more focused on the argument ending with specific, detailed evidence supporting a claim. Lastly, the author explains how and why the information she has just provided connects to and supports her thesis (a brief wrap-up or warrant).

Moving from General to Specific Information
The four elements of a good paragraph (TTEB)
A good paragraph should contain at least the following four elements: T ransition, T opic sentence, specific E vidence and analysis, and a B rief wrap-up sentence (also known as a warrant ) –TTEB!
- A T ransition sentence leading in from a previous paragraph to assure smooth reading. This acts as a hand-off from one idea to the next.
- A T opic sentence that tells the reader what you will be discussing in the paragraph.
- Specific E vidence and analysis that supports one of your claims and that provides a deeper level of detail than your topic sentence.
- A B rief wrap-up sentence that tells the reader how and why this information supports the paper’s thesis. The brief wrap-up is also known as the warrant. The warrant is important to your argument because it connects your reasoning and support to your thesis, and it shows that the information in the paragraph is related to your thesis and helps defend it.
Supporting evidence (induction and deduction)
Induction is the type of reasoning that moves from specific facts to a general conclusion. When you use induction in your paper, you will state your thesis (which is actually the conclusion you have come to after looking at all the facts) and then support your thesis with the facts. The following is an example of induction taken from Dorothy U. Seyler’s Understanding Argument :
There is the dead body of Smith. Smith was shot in his bedroom between the hours of 11:00 p.m. and 2:00 a.m., according to the coroner. Smith was shot with a .32 caliber pistol. The pistol left in the bedroom contains Jones’s fingerprints. Jones was seen, by a neighbor, entering the Smith home at around 11:00 p.m. the night of Smith’s death. A coworker heard Smith and Jones arguing in Smith’s office the morning of the day Smith died.
Conclusion: Jones killed Smith.
Here, then, is the example in bullet form:
- Conclusion: Jones killed Smith
- Support: Smith was shot by Jones’ gun, Jones was seen entering the scene of the crime, Jones and Smith argued earlier in the day Smith died.
- Assumption: The facts are representative, not isolated incidents, and thus reveal a trend, justifying the conclusion drawn.
When you use deduction in an argument, you begin with general premises and move to a specific conclusion. There is a precise pattern you must use when you reason deductively. This pattern is called syllogistic reasoning (the syllogism). Syllogistic reasoning (deduction) is organized in three steps:
- Major premise
- Minor premise
In order for the syllogism (deduction) to work, you must accept that the relationship of the two premises lead, logically, to the conclusion. Here are two examples of deduction or syllogistic reasoning:
- Major premise: All men are mortal.
- Minor premise: Socrates is a man.
- Conclusion: Socrates is mortal.
- Major premise: People who perform with courage and clear purpose in a crisis are great leaders.
- Minor premise: Lincoln was a person who performed with courage and a clear purpose in a crisis.
- Conclusion: Lincoln was a great leader.
So in order for deduction to work in the example involving Socrates, you must agree that (1) all men are mortal (they all die); and (2) Socrates is a man. If you disagree with either of these premises, the conclusion is invalid. The example using Socrates isn’t so difficult to validate. But when you move into more murky water (when you use terms such as courage , clear purpose , and great ), the connections get tenuous.
For example, some historians might argue that Lincoln didn’t really shine until a few years into the Civil War, after many Union losses to Southern leaders such as Robert E. Lee.
The following is a clear example of deduction gone awry:
- Major premise: All dogs make good pets.
- Minor premise: Doogle is a dog.
- Conclusion: Doogle will make a good pet.
If you don’t agree that all dogs make good pets, then the conclusion that Doogle will make a good pet is invalid.
When a premise in a syllogism is missing, the syllogism becomes an enthymeme. Enthymemes can be very effective in argument, but they can also be unethical and lead to invalid conclusions. Authors often use enthymemes to persuade audiences. The following is an example of an enthymeme:
If you have a plasma TV, you are not poor.
The first part of the enthymeme (If you have a plasma TV) is the stated premise. The second part of the statement (you are not poor) is the conclusion. Therefore, the unstated premise is “Only rich people have plasma TVs.” The enthymeme above leads us to an invalid conclusion (people who own plasma TVs are not poor) because there are plenty of people who own plasma TVs who are poor. Let’s look at this enthymeme in a syllogistic structure:
- Major premise: People who own plasma TVs are rich (unstated above).
- Minor premise: You own a plasma TV.
- Conclusion: You are not poor.
To help you understand how induction and deduction can work together to form a solid argument, you may want to look at the United States Declaration of Independence. The first section of the Declaration contains a series of syllogisms, while the middle section is an inductive list of examples. The final section brings the first and second sections together in a compelling conclusion.

Body Paragraph
Ai generator.
Whether you’re crafting an essay , report , or any other form of written communication, the body paragraphs serve as the heart of your composition. They provide the substantive content that supports your main ideas, arguments, or points. Understanding how to construct compelling body paragraphs is essential for conveying your message effectively and persuasively. In this guide, we’ll delve into the definition of body paragraphs, explore the step-by-step process to create them, address common FAQs, and highlight their significance in written communication.
What is a Body Paragraph?
A body paragraph is a section of an essay that develops a single main idea, supported by evidence, examples, and explanations. Each body paragraph typically starts with a topic sentence, followed by supporting details, and concludes with a sentence that reinforces the paragraph’s main point or transitions to the next idea. Effective body paragraphs help to structure and advance the essay’s argument.
Body Paragraph Format
Body paragraphs form the core of an essay, providing the details and evidence that support the thesis statement . A well-structured body paragraph enhances clarity, flow, and persuasiveness in writing . Here’s a guide to constructing effective body paragraphs:
1. Topic Sentence
The topic sentence introduces the main idea of the paragraph. It should be clear, concise, and directly related to the thesis statement.
- Example : “Regular exercise significantly improves mental health.”
2. Explanation
Expand on the topic sentence by providing a brief explanation or elaboration. This helps to clarify the main idea and set up the evidence.
- Example : “Engaging in physical activities releases endorphins, which are natural mood lifters.”
3. Evidence
Present specific evidence to support the main idea. This can include quotes, statistics, examples, or research findings.
- Example : “A study by the Mayo Clinic found that participants who exercised regularly reported a 30% decrease in symptoms of depression and anxiety.”
4. Analysis
Analyze the evidence to show how it supports the topic sentence. Explain the significance and implications of the evidence.
- Example : “This decrease in mental health symptoms highlights the profound impact of physical activity on psychological well-being, suggesting that regular exercise can be an effective non-pharmaceutical treatment for mental health issues.”
5. Transition
Conclude the paragraph by linking back to the thesis or transitioning smoothly to the next paragraph. This helps maintain coherence and flow in the essay.
- Example : “Therefore, incorporating regular exercise into one’s routine can be a crucial step towards improving mental health. Next, we will explore the benefits of exercise on cognitive function.”
Examples of Body Paragraph for Essay
1. the benefits of reading.
Reading regularly enhances cognitive functions. When individuals read, they engage multiple areas of the brain, improving neural connectivity. A study by the University of California found that regular readers exhibit higher levels of brain activity, particularly in areas related to language comprehension and analytical thinking. This increased brain activity suggests that reading not only improves comprehension skills but also enhances critical thinking and problem-solving abilities. Moreover, reading has been linked to a reduced risk of cognitive decline in older adults, further highlighting its long-term benefits. Therefore, incorporating reading into daily routines can significantly boost cognitive health and preserve mental sharpness over time.
2. The Impact of Technology on Education
Technology has revolutionized education by providing greater access to information and resources. With the advent of the internet and digital tools, students can access a vast array of educational materials from anywhere in the world. According to a report by the Pew Research Center, 92% of teachers reported that the internet has a major impact on their ability to access content, resources, and materials for their teaching. This accessibility not only enhances the learning experience but also enables personalized learning, where students can learn at their own pace and according to their interests. Furthermore, educational technologies such as online courses and virtual classrooms have made education more inclusive, reaching students in remote and underserved areas. Consequently, the integration of technology in education has democratized learning, making it more accessible and tailored to individual needs.
3. The Importance of Environmental Conservation
Environmental conservation is crucial for sustaining biodiversity and ensuring the health of our planet. Ecosystems are interdependent, and the loss of one species can have a ripple effect on others. For instance, the decline of bee populations, which are vital pollinators, has significant implications for plant reproduction and agricultural productivity. According to the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), 75% of the world’s food crops depend, at least in part, on pollination by bees and other insects. This interdependence underscores the importance of protecting species to maintain ecological balance and food security. Additionally, conserving natural habitats helps mitigate climate change by preserving forests that act as carbon sinks. Therefore, concerted efforts in environmental conservation are essential for the well-being of all life forms on Earth and the stability of our ecosystems.
4. The Advantages of Learning a Second Language
Learning a second language enhances cognitive abilities and cultural understanding. Bilingual individuals often exhibit improved memory, problem-solving skills, and multitasking abilities. Research from Pennsylvania State University indicates that bilingualism can delay the onset of Alzheimer’s disease by up to five years. This cognitive boost is attributed to the mental exercise of switching between languages and processing complex linguistic structures. Moreover, learning a new language fosters cultural empathy and global awareness. It allows individuals to better understand and appreciate cultural differences, promoting tolerance and reducing prejudice. In an increasingly interconnected world, these skills are invaluable, making bilingualism a significant asset both personally and professionally.
5. The Role of Physical Exercise in Health
Physical exercise plays a pivotal role in maintaining overall health and well-being. Regular physical activity helps control weight, reduce the risk of chronic diseases, and improve mental health. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) states that adults who engage in moderate-intensity exercise for at least 150 minutes per week lower their risk of heart disease, stroke, and diabetes. Additionally, exercise promotes the release of endorphins, which are natural mood lifters, reducing symptoms of depression and anxiety. Engaging in physical activities also enhances sleep quality, boosts energy levels, and improves muscle and bone strength. Consequently, incorporating regular exercise into one’s lifestyle is essential for physical and mental health, leading to a better quality of life.
Examples of Body Paragraph for Argumentative Essay
1. the case for universal healthcare.
Universal healthcare is essential for ensuring that all citizens have access to necessary medical services. In countries with universal healthcare, individuals do not have to worry about the financial burden of medical expenses, which can lead to better overall public health outcomes. For instance, a study conducted by the Commonwealth Fund found that countries with universal healthcare systems, such as Canada and the United Kingdom, have higher life expectancy and lower infant mortality rates compared to the United States. This data suggests that when people have access to healthcare without financial barriers, they are more likely to seek preventive care and treatment for illnesses, leading to healthier populations. Moreover, universal healthcare can reduce economic inequality by alleviating the financial strain on low-income families who might otherwise be unable to afford medical care. Therefore, implementing a universal healthcare system is a necessary step towards a healthier, more equitable society.
2. The Need for Renewable Energy
Investing in renewable energy sources is crucial for combating climate change and ensuring sustainable development. Fossil fuels, such as coal and oil, contribute significantly to greenhouse gas emissions, which are the primary drivers of global warming. According to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), renewable energy sources like wind, solar, and hydropower produce little to no greenhouse gases during operation. This makes them a much cleaner alternative to traditional energy sources. Additionally, the renewable energy sector has the potential to create millions of jobs worldwide. The International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA) reports that the renewable energy industry employed over 11 million people globally in 2018, a number that is expected to grow as investment in this sector increases. By transitioning to renewable energy, we can significantly reduce our carbon footprint while also fostering economic growth and job creation. Therefore, prioritizing renewable energy investments is imperative for a sustainable future.
3. The Benefits of Online Education
Online education provides greater accessibility and flexibility for students, making it an invaluable tool in modern education. Traditional classroom settings can be restrictive for individuals who have other commitments such as work or family. A report by the National Center for Education Statistics (NCES) shows that the number of students enrolled in at least one online course has steadily increased over the past decade, reaching over 6 million in the United States alone. This rise in online education enrollment demonstrates its growing popularity and effectiveness. Furthermore, online education allows for a personalized learning experience where students can learn at their own pace and revisit material as needed. Studies from the U.S. Department of Education suggest that students in online learning conditions performed modestly better, on average, than those receiving face-to-face instruction. Therefore, embracing online education can enhance learning opportunities and outcomes for a diverse range of students.
4. The Importance of Animal Testing in Medical Research
Animal testing remains a necessary practice for advancing medical research and ensuring the safety of new treatments. Many medical breakthroughs, including vaccines and life-saving treatments, have been developed through research conducted on animals. For instance, the polio vaccine, which has nearly eradicated the disease globally, was developed through extensive animal testing. Without such testing, it would have been impossible to ensure the vaccine’s effectiveness and safety. Moreover, regulatory agencies like the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) require animal testing to evaluate the safety of new drugs before they can be approved for human trials. This process helps protect human participants from potential adverse effects. While it is crucial to continue seeking alternative methods, current scientific capabilities still rely on animal testing to a significant extent. Therefore, until reliable and effective alternatives are found, animal testing remains an essential component of medical research.
5. The Impact of Social Media on Society
Social media has a profound impact on society, influencing everything from communication to mental health. Platforms like Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram have revolutionized the way people interact, share information, and stay connected. However, research indicates that excessive use of social media can lead to negative mental health outcomes. A study published in the Journal of Social and Clinical Psychology found that individuals who limited their social media use to 30 minutes per day reported significant reductions in feelings of loneliness and depression. This suggests that while social media can facilitate connection, overuse can exacerbate feelings of isolation and anxiety. Additionally, the spread of misinformation on social media platforms poses a significant threat to public discourse and democratic processes. Therefore, it is essential to promote responsible use of social media and implement measures to combat misinformation to mitigate its negative impacts on society.
Examples of Body Paragraph for Informative Essay
1. the history of the internet.
The internet has a rich history that dates back to the early days of computer networking. The concept of a global network began in the 1960s with the creation of ARPANET, funded by the United States Department of Defense. ARPANET, which stands for Advanced Research Projects Agency Network, was the first network to implement the TCP/IP protocol suite, which became the foundation of the modern internet. In the 1980s, the development of personal computers and the World Wide Web, invented by Tim Berners-Lee in 1989, revolutionized how information was shared and accessed. The introduction of web browsers, like Mosaic and Netscape, in the early 1990s made the internet more user-friendly and accessible to the general public. This period marked the beginning of the internet’s rapid expansion and integration into everyday life, leading to the interconnected digital world we experience today.
2. The Benefits of a Balanced Diet
A balanced diet is essential for maintaining good health and well-being. Consuming a variety of foods ensures that the body receives the necessary nutrients it needs to function properly. For example, fruits and vegetables are rich in vitamins and minerals, which support immune function and reduce the risk of chronic diseases. Protein-rich foods, such as lean meats, beans, and nuts, are crucial for muscle repair and growth, while whole grains provide sustained energy and help regulate blood sugar levels. According to the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, a balanced diet that includes a wide range of nutrients can improve overall health and reduce the risk of conditions like heart disease, diabetes, and obesity. Furthermore, staying hydrated by drinking plenty of water is also a key component of a balanced diet, as it aids digestion and helps maintain body temperature. Therefore, incorporating a variety of nutrient-rich foods into one’s diet is fundamental to achieving and maintaining optimal health.
3. The Role of Technology in Modern Education
Technology plays a pivotal role in modern education, transforming the way students learn and teachers instruct. With the advent of digital tools and online resources, educational opportunities have expanded significantly. For instance, interactive software and applications make learning more engaging and personalized, catering to individual student needs. According to a report by the National Education Association (NEA), technology in the classroom has been shown to improve student motivation and academic performance. Moreover, online learning platforms, such as Coursera and Khan Academy, provide access to a vast array of courses and educational materials, enabling lifelong learning beyond the traditional classroom setting. These resources allow students to learn at their own pace and revisit difficult concepts as needed. Consequently, the integration of technology in education not only enhances learning experiences but also prepares students for a digital future.
4. The Importance of Environmental Conservation
Environmental conservation is crucial for preserving the planet’s biodiversity and natural resources. Human activities, such as deforestation, pollution, and overfishing, have led to significant environmental degradation. For example, the destruction of rainforests not only results in the loss of countless species but also contributes to climate change by reducing the Earth’s capacity to absorb carbon dioxide. The World Wildlife Fund (WWF) reports that approximately 27% of the Amazon rainforest has been destroyed in the past 50 years, posing a severe threat to global biodiversity. Conservation efforts, such as protecting natural habitats, promoting sustainable practices, and reducing carbon emissions, are essential to mitigate these impacts. By implementing and supporting conservation initiatives, we can help ensure that natural ecosystems remain intact for future generations. Therefore, environmental conservation is a responsibility that must be shared by individuals, communities, and governments worldwide.
5. The Advantages of Learning a Second Language
Learning a second language offers numerous cognitive, social, and professional benefits. Research indicates that bilingual individuals often have better cognitive flexibility, which is the ability to switch between tasks and think about multiple concepts simultaneously. A study published in the journal Psychological Science found that bilingualism can enhance executive function, which includes skills such as problem-solving, memory, and attention control. In addition to cognitive advantages, knowing a second language can improve cultural awareness and communication skills. This is particularly valuable in today’s globalized world, where cross-cultural interactions are common. Professionally, bilingualism can open up job opportunities and enhance career prospects in various fields, such as international business, translation, and diplomacy. Therefore, investing time and effort in learning a second language can yield significant personal and professional rewards.
Examples of Body Paragraph for Research Paper
1. the effects of climate change on polar bear populations.
Climate change has significantly impacted polar bear populations, primarily through the loss of their sea ice habitat. Polar bears rely on sea ice as a platform for hunting seals, their primary food source. According to a study by the National Snow and Ice Data Center (NSIDC), the Arctic sea ice extent has declined by approximately 13% per decade since the late 1970s. This reduction in sea ice forces polar bears to travel greater distances and expend more energy to find food, leading to malnutrition and decreased survival rates, especially among cubs. Moreover, a report by the World Wildlife Fund (WWF) indicates that the shrinking ice habitat also increases the likelihood of human-polar bear conflicts as bears venture closer to human settlements in search of food. These findings underscore the urgent need for comprehensive climate policies to mitigate the effects of global warming and protect polar bear populations.
2. The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare
Artificial intelligence (AI) has revolutionized healthcare by enhancing diagnostic accuracy and improving patient outcomes. AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of medical data, identifying patterns that may not be evident to human clinicians. For instance, a study published in Nature Medicine demonstrated that an AI system could diagnose skin cancer with greater accuracy than dermatologists, achieving a sensitivity rate of 95% compared to 86.6% for human experts. This capability allows for earlier detection and treatment of diseases, potentially saving lives. Additionally, AI-driven predictive analytics can help in managing chronic conditions by forecasting disease progression and suggesting personalized treatment plans. According to a report by Accenture, AI applications in healthcare could save the U.S. healthcare economy up to $150 billion annually by 2026 through efficiencies and improved outcomes. These advancements highlight the transformative potential of AI in making healthcare more efficient, accurate, and accessible.
3. The Impact of Social Media on Political Polarization
Social media has played a significant role in exacerbating political polarization by creating echo chambers and facilitating the spread of misinformation. Algorithms on platforms like Facebook and Twitter often promote content that aligns with users’ existing beliefs, reinforcing their viewpoints and isolating them from opposing perspectives. A study by the Pew Research Center found that 62% of Americans get their news from social media, where they are more likely to encounter sensationalized and biased information. This selective exposure can deepen ideological divides and reduce the likelihood of constructive political discourse. Moreover, research published in Science revealed that false news stories on social media spread six times faster than true stories, further fueling division and mistrust. These findings indicate that social media not only mirrors but also amplifies societal divisions, necessitating interventions to promote media literacy and responsible content sharing.
4. The Benefits of Bilingual Education Programs
Bilingual education programs offer significant cognitive and academic benefits to students. Studies have shown that bilingual individuals possess enhanced executive function, which includes skills such as problem-solving, multitasking, and memory. For example, research conducted by the American Psychological Association (APA) indicates that bilingual children outperform monolingual peers in tasks that require switching attention and inhibiting distractions. These cognitive advantages translate into academic success, with bilingual students often achieving higher scores in standardized tests. Additionally, a longitudinal study by the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) found that students enrolled in dual-language programs were more likely to graduate high school and attend college compared to their monolingual counterparts. These outcomes suggest that bilingual education not only supports cognitive development but also enhances long-term educational achievement. Therefore, expanding access to bilingual programs can provide substantial benefits to students and society as a whole.
5. The Economic Impact of Renewable Energy Adoption
Adopting renewable energy sources has significant positive impacts on the economy, including job creation and energy security. The transition to renewable energy requires a substantial workforce to manufacture, install, and maintain technologies such as solar panels and wind turbines. According to the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA), the renewable energy sector employed over 11 million people globally in 2018, with job numbers expected to rise as investment in this sector increases. This job creation can stimulate economic growth, particularly in regions struggling with unemployment. Furthermore, renewable energy reduces dependence on imported fuels, enhancing national energy security and price stability. A report by the U.S. Department of Energy highlights that increased use of domestic renewable energy sources can protect the economy from fluctuations in global fossil fuel markets. Thus, the economic benefits of renewable energy adoption extend beyond environmental considerations, offering substantial advantages for employment and national security.
Examples of Body Paragraph for Students
1. the importance of time management for students.
Effective time management is crucial for students to achieve academic success and maintain a healthy work-life balance. Properly managing time allows students to prioritize tasks, ensuring that important assignments and study sessions are completed efficiently. For instance, a study by the University of California, Berkeley found that students who practiced time management techniques, such as using planners and setting specific goals, achieved higher grades and reported lower stress levels. By breaking down larger tasks into smaller, manageable steps, students can avoid last-minute cramming and reduce anxiety. Moreover, time management skills are not only beneficial for academic purposes but also for extracurricular activities and personal life. Students who balance their schedules effectively can participate in sports, hobbies, and social events, contributing to their overall well-being and personal development. Therefore, mastering time management is essential for students to succeed academically and enjoy a balanced lifestyle.

2. The Benefits of Extracurricular Activities
Participating in extracurricular activities offers numerous benefits that enhance students’ educational experiences and personal growth. Engaging in activities such as sports, clubs, and arts programs helps students develop essential skills that are not typically taught in the classroom. For example, involvement in team sports teaches valuable lessons in teamwork, leadership, and perseverance. According to a report by the National Center for Education Statistics (NCES), students who participate in extracurricular activities are more likely to have higher academic achievement and better attendance records. These activities also provide opportunities for students to explore their interests and talents, which can influence their future career choices and aspirations. Additionally, extracurricular involvement fosters a sense of belonging and community, helping students build friendships and support networks. Thus, engaging in extracurricular activities is instrumental in promoting well-rounded development and enriching the overall educational experience for students.
3. The Impact of Nutrition on Academic Performance
Proper nutrition plays a vital role in students’ academic performance and overall health. Consuming a balanced diet that includes a variety of nutrients helps maintain energy levels, improve concentration, and enhance cognitive function. A study published in the Journal of School Health found that students who ate a nutritious breakfast performed better on standardized tests and had higher attendance rates compared to those who skipped breakfast. Healthy eating habits also contribute to better mood regulation and reduced stress, which are important for academic success. For instance, foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, such as fish and flaxseeds, have been shown to support brain health and improve memory. Schools that implement nutrition education programs and provide healthy meal options can significantly impact students’ learning outcomes. Therefore, promoting proper nutrition is essential for students to achieve their full academic potential and maintain overall well-being.
4. The Advantages of Using Technology in the Classroom
Integrating technology into the classroom offers numerous advantages that enhance the learning experience for students. Digital tools and resources make learning more interactive and engaging, catering to different learning styles and needs. For instance, educational apps and online platforms allow students to practice skills at their own pace and receive immediate feedback. According to a report by the U.S. Department of Education, schools that utilize technology effectively see improvements in student motivation and achievement. Technology also facilitates access to a wealth of information and educational materials, enabling students to conduct research and expand their knowledge beyond the textbook. Furthermore, incorporating technology prepares students for the digital world, equipping them with essential skills for future careers. Thus, the use of technology in education not only enhances academic performance but also prepares students for success in a technologically advanced society.
5. The Importance of Reading for Pleasure
Reading for pleasure is an important habit that benefits students academically and personally. Engaging in recreational reading improves literacy skills, vocabulary, and comprehension. A study by the National Literacy Trust found that students who read for enjoyment are more likely to perform better academically, particularly in language and literacy subjects. Additionally, reading for pleasure enhances creativity and imagination, allowing students to explore new ideas and perspectives. For example, reading fiction can increase empathy by helping students understand and relate to characters’ experiences and emotions. Beyond academic benefits, reading provides a relaxing escape from the pressures of school and daily life, promoting mental well-being. Therefore, encouraging students to read for pleasure is essential for their overall development and success.
More Examples & Samples of Body Paragraph in PDF
1. developing body paragraphs example.
2. Strong Body Paragraphs Example

3. Body Paragraph Structure and Development

4. Basic Body Paragraphs Example

5. How to Write Body Paragraphs Example

6. Purpose of a Body Paragraph Example

Parts of a Body Paragraph
A well-constructed body paragraph is essential for a coherent and persuasive essay. Each body paragraph should support the main thesis of the essay and contribute to the overall argument or analysis. Here are the key parts of a body paragraph:
The topic sentence introduces the main idea of the paragraph. It should be clear, concise, and directly related to the thesis statement of the essay.
- Example : “Effective time management is crucial for students to achieve academic success.”
The explanation elaborates on the topic sentence, providing context or a brief overview of the main idea. It sets up the evidence and analysis that will follow.
- Example : “Properly managing time allows students to prioritize tasks, ensuring that important assignments and study sessions are completed efficiently.”
Evidence provides specific support for the main idea. This can include quotes, statistics, examples, or research findings. Evidence makes the argument more credible and persuasive.
- Example : “A study by the University of California, Berkeley found that students who practiced time management techniques, such as using planners and setting specific goals, achieved higher grades and reported lower stress levels.”
The analysis explains how the evidence supports the topic sentence. It connects the evidence to the main idea and shows the significance or implications of the evidence.
- Example : “By breaking down larger tasks into smaller, manageable steps, students can avoid last-minute cramming and reduce anxiety, leading to better academic performance.”
5. Transition or Concluding Sentence
The transition or concluding sentence links back to the thesis or sets up the next paragraph. It ensures coherence and flow in the essay.
- Example : “Therefore, mastering time management is essential for students to succeed academically and enjoy a balanced lifestyle.”
How to Start a Body Paragraph
Starting a body paragraph effectively is essential for maintaining coherence and ensuring that each paragraph contributes meaningfully to the essay. Here are key steps and tips for starting a body paragraph:
1. Craft a Strong Topic Sentence
The topic sentence is the most important part of the body paragraph. It introduces the main idea of the paragraph and ties it to the thesis statement.
- Example : “Implementing renewable energy sources is essential for reducing greenhouse gas emissions.”
2. Connect to the Thesis Statement
Ensure that the topic sentence clearly relates to and supports the essay’s thesis statement. This connection helps maintain the overall coherence of the essay.
- Example : “Given the urgent need to address climate change, implementing renewable energy sources is essential for reducing greenhouse gas emissions.”
3. Use Transition Words or Phrases
If the paragraph follows another body paragraph, use transition words or phrases to create a smooth flow of ideas. This helps guide the reader through the argument or analysis.
- Example : “Moreover, implementing renewable energy sources is essential for reducing greenhouse gas emissions.”
4. Introduce the Main Idea Clearly
State the main idea in a way that is easy to understand and sets up the explanation and evidence that will follow.
- Example : “Implementing renewable energy sources is essential for reducing greenhouse gas emissions, as it offers a sustainable alternative to fossil fuels.”
How to End a Body Paragraph
Ending a body paragraph effectively is crucial for maintaining the flow and coherence of your essay. A strong concluding sentence can reinforce your main point, connect to the thesis, and provide a smooth transition to the next paragraph. Here are key steps and tips for ending a body paragraph:
1. Summarize the Main Point
Briefly restate the main idea of the paragraph without repeating it verbatim. This reinforces the point you’ve made.
- Example : “Therefore, renewable energy sources are essential for reducing greenhouse gas emissions.”
2. Connect to the Thesis
Ensure that the concluding sentence links back to the thesis statement, reinforcing how the paragraph supports the overall argument.
- Example : “This reduction in emissions is a critical step in combating climate change, aligning with the global effort to create a more sustainable future.”
3. Provide a Transition
Use a transitional phrase or sentence to smoothly lead into the next paragraph. This helps maintain coherence and guides the reader through your essay.
- Example : “As we explore further, the economic benefits of renewable energy adoption also become apparent.”
4. Avoid Introducing New Information
Do not introduce new arguments or evidence in the concluding sentence. The focus should be on wrapping up the current paragraph and preparing for the next one.
How to Write a Body Paragraph

1. Start with a Topic Sentence
- Purpose : Introduce the main idea of the paragraph.
- Example : “One of the most significant advantages of renewable energy is its positive impact on the environment.”
2. Provide an Explanation
- Purpose : Clarify the topic sentence and provide context.
- Example : “Renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, produce little to no greenhouse gas emissions during their operation.”
3. Present Evidence
- Purpose : Support the main idea with relevant data, quotes, or examples.
- Example : “According to a 2020 report by the International Energy Agency, solar power capacity grew by 22% worldwide, reducing CO2 emissions by approximately 1.2 billion tons annually.”
4. Include Analysis
- Purpose : Explain how the evidence supports the main idea.
- Example : “This significant reduction in emissions highlights how transitioning to renewable energy sources can mitigate climate change, a pressing global issue.”
5. Conclude with a Closing Sentence
- Purpose : Summarize the paragraph’s main point and transition to the next paragraph.
- Example : “Therefore, the shift to renewable energy is not only beneficial for reducing environmental harm but also essential for sustainable development.”
How long should a body paragraph be?
A body paragraph typically ranges from 5-8 sentences or 150-200 words, balancing detail and clarity without overwhelming the reader.
What is the purpose of a topic sentence?
A topic sentence introduces the main idea of the paragraph and sets the tone for the content that follows.
How can I ensure coherence in my body paragraph?
Use transitional words and phrases, maintain a logical flow of ideas, and ensure all sentences relate to the main idea.
What types of evidence can I use?
Use facts, statistics, quotes, examples, and anecdotes from credible sources to support your main idea effectively.
Why is analysis important in a body paragraph?
Analysis explains how your evidence supports your main idea, demonstrating critical thinking and deepening the reader’s understanding.
How do I transition between body paragraphs?
Use transitional sentences or phrases that connect the ideas of consecutive paragraphs, maintaining a smooth flow throughout your essay.
What should a closing sentence do?
A closing sentence should summarize the paragraph’s main point and provide a transition to the next paragraph.
Can I use personal experiences as evidence?
Yes, personal anecdotes can be powerful evidence, especially in narrative or persuasive essays, if they are relevant and support your point.
How many body paragraphs should an essay have?
The number of body paragraphs depends on the essay’s length and complexity, but typically ranges from 3-5 for standard essays.
What common mistakes should I avoid in body paragraphs?
Avoid vague topic sentences, lack of evidence, poor transitions, and irrelevant details that do not support the main idea.
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
- Humanities ›
- English Grammar ›
Definition and Examples of Body Paragraphs in Composition
Peter Dazeley / Getty Images
- An Introduction to Punctuation
- Ph.D., Rhetoric and English, University of Georgia
- M.A., Modern English and American Literature, University of Leicester
- B.A., English, State University of New York
The body paragraphs are the part of an essay , report , or speech that explains and develops the main idea (or thesis ). They come after the introduction and before the conclusion . The body is usually the longest part of an essay, and each body paragraph may begin with a topic sentence to introduce what the paragraph will be about.
Taken together, they form the support for your thesis, stated in your introduction. They represent the development of your idea, where you present your evidence.
"The following acronym will help you achieve the hourglass structure of a well-developed body paragraph:
- T opic Sentence (a sentence that states the one point the paragraph will make)
- A ssertion statements (statements that present your ideas)
- e X ample(s) (specific passages, factual material, or concrete detail)
- E xplanation (commentary that shows how the examples support your assertion)
- S ignificance (commentary that shows how the paragraph supports the thesis statement).
TAXES gives you a formula for building the supporting paragraphs in a thesis-driven essay." (Kathleen Muller Moore and Susie Lan Cassel, Techniques for College Writing: The Thesis Statement and Beyond . Wadsworth, 2011)
Organization Tips
Aim for coherence to your paragraphs. They should be cohesive around one point. Don't try to do too much and cram all your ideas in one place. Pace your information for your readers, so that they can understand your points individually and follow how they collectively relate to your main thesis or topic.
Watch for overly long paragraphs in your piece. If, after drafting, you realize that you have a paragraph that extends for most of a page, examine each sentence's topic, and see if there is a place where you can make a natural break, where you can group the sentences into two or more paragraphs. Examine your sentences to see if you're repeating yourself, making the same point in two different ways. Do you need both examples or explanations?
Paragraph Caveats
A body paragraph doesn't always have to have a topic sentence. A formal report or paper is more likely to be structured more rigidly than, say, a narrative or creative essay, because you're out to make a point, persuade, show evidence backing up an idea, or report findings.
Next, a body paragraph will differ from a transitional paragraph , which serves as a short bridge between sections. When you just go from paragraph to paragraph within a section, you likely will just need a sentence at the end of one to lead the reader to the next, which will be the next point that you need to make to support the main idea of the paper.
Examples of Body Paragraphs in Student Essays
Completed examples are often useful to see, to give you a place to start analyzing and preparing for your own writing. Check these out:
- How to Catch River Crabs (paragraphs 2 and 3)
- Learning to Hate Mathematics (paragraphs 2-4)
- Rhetorical Analysis of U2's "Sunday Bloody Sunday" (paragraphs 2-13)
- Understanding General-to-Specific Order in Composition
- Development in Composition: Building an Essay
- Definition and Examples of Transitional Paragraphs
- Padding and Composition
- Definition and Examples of Paragraph Breaks in Prose
- Definition and Examples of Climactic Order in Composition and Speech
- Understanding Organization in Composition and Speech
- Conclusion in Compositions
- Unity in Composition
- Paragraph Length in Compositions and Reports
- A Critical Analysis of George Orwell's 'A Hanging'
- Definition and Examples of Spacing in Composition
- Best Practices for the Most Effective Use of Paragraphs
- 7 Secrets to Success in English 101
- The Parts of a Speech in Classical Rhetoric
- Definition and Examples of Paragraphing in Essays

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A body paragraph is any paragraph in the middle of an essay, paper, or article that comes after the introduction but before the conclusion.Generally, body paragraphs support the work's thesis and shed new light on the main topic, whether through empirical data, logical deduction, deliberate persuasion, or anecdotal evidence.
A body paragraph has three major components: (1) topic sentence, (2) explanation, (3) supporting details.Without any of them, the body paragraph seems to be missing something, and will not add anything to the theme and central idea of the essay.. Topic Sentence The topic sentence is the first sentence of a paragraph, and states the main idea to be discussed in the paragraph.
A strong paragraph in an academic essay will usually include these three elements: A topic sentence. The topic sentence does double duty for a paragraph. First, a strong topic sentence makes a claim or states a main idea that is then developed in the rest of the paragraph. Second, the topic sentence signals to readers how the paragraph is ...
A good paragraph has a basic structure with three main components: . 1. A topic sentence: A topic sentence, or key sentence, is the first sentence of your paragraph that prepares your audience for the information to come.Each body paragraph should have its own topic sentence outlining the ensuing ideas. Topic sentences are especially useful for body paragraphs that pivot to new information.
The body is the longest part of an essay. This is where you lead the reader through your ideas, elaborating arguments and evidence for your thesis. The body is always divided into paragraphs. You can work through the body in three main stages: Create an outline of what you want to say and in what order.
Body paragraphs: Moving from general to specific information. Your paper should be organized in a manner that moves from general to specific information. Every time you begin a new subject, think of an inverted pyramid - The broadest range of information sits at the top, and as the paragraph or paper progresses, the author becomes more and more ...
If it's more complicated, you'll need more body paragraphs. An easy way to remember the parts of a body paragraph is to think of them as the MEAT of your essay: Main Idea. The part of a topic sentence that states the main idea of the body paragraph. All of the sentences in the paragraph connect to it. Keep in mind that main ideas are ...
This section is the backbone of any essay. A well-organized structure of the body paragraph helps your writing be readable. That's why organizing the information to achieve this goal is essential. When writing body paragraphs in an essay, you focus on presenting and developing one point that supports the main argument.
A well-constructed body paragraph is essential for a coherent and persuasive essay. Each body paragraph should support the main thesis of the essay and contribute to the overall argument or analysis. Here are the key parts of a body paragraph: 1. Topic Sentence. The topic sentence introduces the main idea of the paragraph.
The body paragraphs are the part of an essay, report, or speech that explains and develops the main idea (or thesis). They come after the introduction and before the conclusion. The body is usually the longest part of an essay, and each body paragraph may begin with a topic sentence to introduce what the paragraph will be about.